Assembly Programming Language
Assignment
- Contents
- What is Assembly Language?
- Why to use Assembly language?
- Direct Hardware Integration
- Optimized Code
- Customization
- Where to use Assembly language?
- Direct Hardware Interaction
- Device Drivers
- Firmware Development
- Performance Optimization
- Critical Performance Code
- Real-Time Systems
- Legacy Systems
- Maintaining Legacy Code
- Reverse Engineering and Security
- Malware Analysis
- Vulnerability Research
- Low-Level Programming
- Bootloaders
- Bare-Metal Programming
- Processor-Specific Instructions
- Custom Instructions
- Optimizing Algorithms
- How to learn coding from start?
- Understand what programming is?
- Why learn to code?
- Career Opportunities
- Problem Solving
- Creativity
- Personal Growth
- Choose a Programming Language
- Explore Learning Resources
- Online Courses
- Video Tutorials:
- Books and E-books
- Understand Basics of chosen language
- Computer Architecture
- Data Basics
- Control Flow
- Text Editors and Terminals
- Practice what you learn
- Code Every Day
- Projects
- Build from Scratch
- Learn from Existing Code
- Interactive Coding Games
What is Assembly Language?
Assembly Language, also known as symbolic machine code, is a low-level programming language that serves as an intermediary between human-readable code and the binary instructions executed by a computer’s hardware.
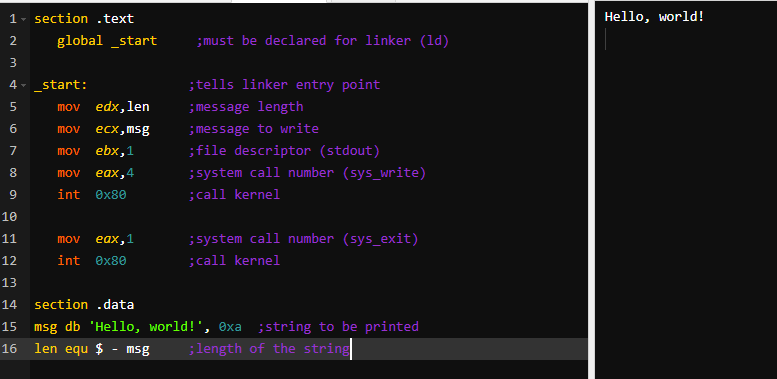
Why to use Assembly language?
Assembly Language serves as a powerful tool for developers, offerings several advantages and use cases. Let’s discuss about its advantages:
Direct Hardware Integration
- Assembly Language allows programmers to communicate directly with a computer’s hardware components.
- It provides precise control over hardware resources, such as registers and memory.
- This direct integration is crucial for tasks like writing device drivers or optimizing code for specific hardware.
Optimized Code
- Assembly instructions map directly to machine language instructions executed by the CPU.
- Programmers can write highly optimized code tailored to the specific hardware.
- Compared to higher-level languages, assembly programs can run faster and more efficiently.
Customization
- Assembly language lets programmers create tailored solutions for hardware issues.
- It’s ideal for systems programming, where code interacts with the operating system and hardware devices.
- For instance, device-specific optimizations can be achieved in assembly language.
Where to use Assembly language?
Assembly language finds its relevance in various contexts due to its unique characteristics. Let’s explore where it is commonly used:
Direct Hardware Interaction
Device Drivers
Assembly language is essential for writing device drivers that allow hardware components (such as printers, graphics cards, or network adapters) to communicate with the operating system.
Firmware Development
Embedded systems, microcontrollers, and Internet of things devices often rely on assembly for firmware development.
Performance Optimization
Critical Performance Code
When performance is crucial, assembly language allows fine-tuning of code for specific hardware architectures.
Real-Time Systems
Applications requiring real-time responsiveness (e.g., robotics, aerospace, or industrial control systems) benefit from assembly’s low-level control.
Legacy Systems
Maintaining Legacy Code
Older systems or software written in assembly may still be in use. Maintenance and updates often require familiarity with assembly language.
Reverse Engineering and Security
Malware Analysis
Security professionals use assembly to analyze and understand malicious code.
Vulnerability Research
Reverse engineers examine binaries to identify security vulnerabilities.
Low-Level Programming
Bootloaders
Assembly is used to create bootloaders that initialize the system during startup.
Bare-Metal Programming
Writing code without an operating system, directly interacting with hardware, is common in assembly.
Processor-Specific Instructions
Custom Instructions
Some processors have unique instructions not available in high-level languages. Assembly allows developers to utilize these instructions.
Optimizing Algorithms
Assembly can optimize specific algorithms by leveraging processor-specific features.
How to learn coding from start?
Learning to code is an exciting journey that opens up a world of possibilities. Here I will explain the ideal path that you can use to start learning code from scratch:
Understand what programming is?
- Programming involves designing and building programs that computers can execute.
- Think of it like cooking: you have an idea for a meal, gather ingredients, prepare the food, and serve it. Similarly, programming turns ideas into functional software.
Why learn to code?
Career Opportunities
Coding skills are in high demand across various industries.
Problem Solving
Coding enhances your problem-solving abilities.
Creativity
You can create software, apps, games, and more.
Personal Growth
Learning to code expands your mind and boosts confidence.
Choose a Programming Language
- Start with a beginner-friendly language like Python or JavaScript.
- Python is versatile, readable, and widely used.
- JavaScript is essential for web development.
Explore Learning Resources
Online Courses
Platforms like freeCodeCamp, Codecademy, and Coursera offer interactive coding courses.
Video Tutorials:
YouTube has countless coding tutorials.
Books and E-books
Read beginner-friendly programming books.
Understand Basics of chosen language
Computer Architecture
Learn how computers process instructions.
Data Basics
Understand variables, data types, and operators.
Control Flow
Learn about loops and conditional statements.
Text Editors and Terminals
- Familiarize yourself with text editors like Visual Studio Code or Sublime Text.
- Learn basic command-line operations.
Practice what you learn
Code Every Day
Consistency is key. Write code regularly.
Projects
Build small projects to apply what you’ve learned.
Build from Scratch
Create something original. You will find hidden errors and your problem solving skill improve by solving these problems
Learn from Existing Code
Study open-source projects. You can find them on GitHub.
Interactive Coding Games
Platforms like HackerRank and LeetCode offer coding challenges.


I am a versatile digital marketing professional with expertise in Search Engine Marketing (SEM), Content Marketing, Blogging, Advertising, Brand Marketing, Digital Marketing, Search Engine Optimization (SEO), and Social Media Marketing. My skill set allows me to create strategies that enhance online visibility, drive traffic, and foster brand loyalty.
